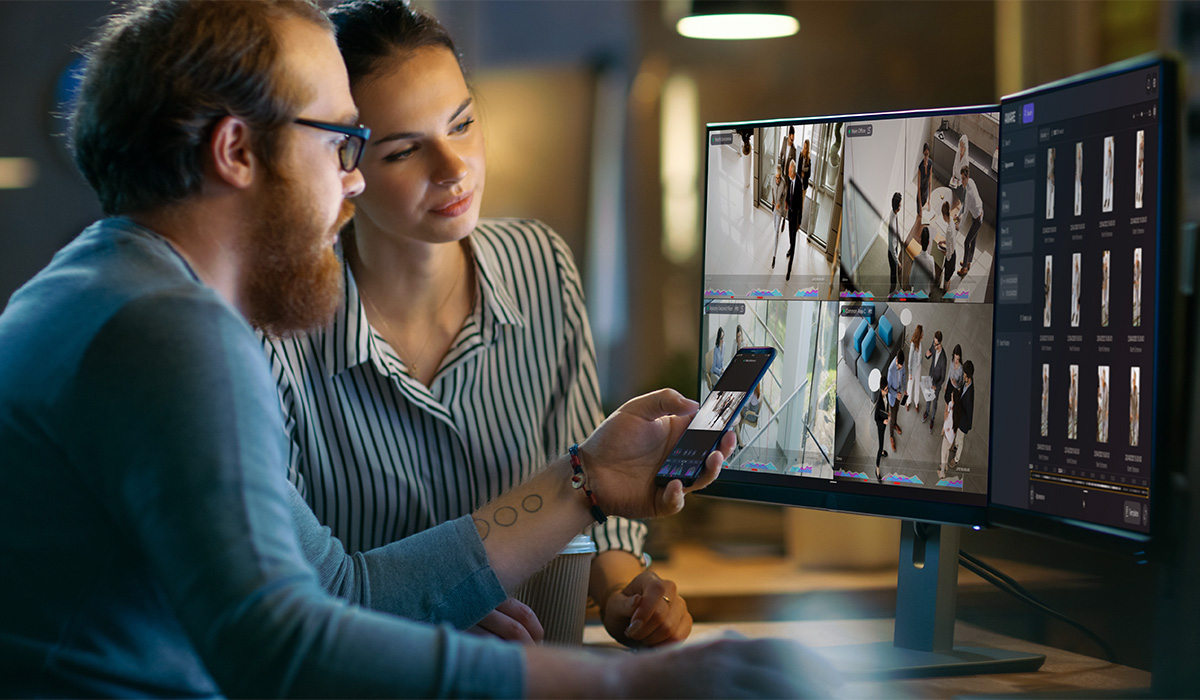
According to the 2024 State of Cloud Physical Security survey, more than 80% of security leaders think that AI video analytics will have a significant influence on the future of proactive physical security solutions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative force in the realm of video analytics, reshaping how we approach video surveillance and operational workflows today. From school hallways to retail stores to parking garages, AI-driven video surveillance is not just about watching, it’s about understanding, optimizing, and predicting. In this blog post, we uncover how AI video analytics are making environments safer and operations smoother across a multitude of industries.
The Evolution of Video Analytics
Video analytics has transformed the way we approach security and surveillance. Originally, the technology was simple, focusing mainly on detecting motion in video footage. This was helpful but limited, as it couldn’t tell the difference between a cat scampering across a parking lot and a person breaking into a car. As technology advanced, especially in the early 2000s with the rise of digital video, video analytics began to incorporate more sophisticated tools, like detecting specific objects (like cars or bags left unattended) and counting people in an area.
The real game-changer came with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into video surveillance. AI has propelled video analytics into a new era, allowing systems to not only see, but understand and interpret what they are watching. These systems use a type of AI called deep learning to analyze video content in real-time. They can differentiate between a wide variety of objects and actions, recognize faces, and even predict potential security threats by noticing unusual patterns of behavior. For instance, if someone lingers too long near a restricted area, the system can alert security personnel to check it out.
How does it work in practice? Imagine a network of cameras continuously feeding video to an AI-driven system. This system scrutinizes each frame of video, identifying and categorizing different elements in the scene—be it a person, a vehicle, or a package. If something out of the ordinary is detected, like someone trying to climb over a fence at night, the system immediately flags this activity. This proactive approach enhances security and ensures that security teams can focus their attention where it’s most needed, making the process more efficient and effective. AI-powered video analytics makes surveillance smarter, helping keep spaces safer with far less effort.
Exploring Video Analytics Technologies
Video analytics includes a wide array of technologies, each tailored to improve video surveillance capabilities. We explore four categories of analytics that have been widely adopted due to their significant impact on enhancing security and operational efficiency across various industries.
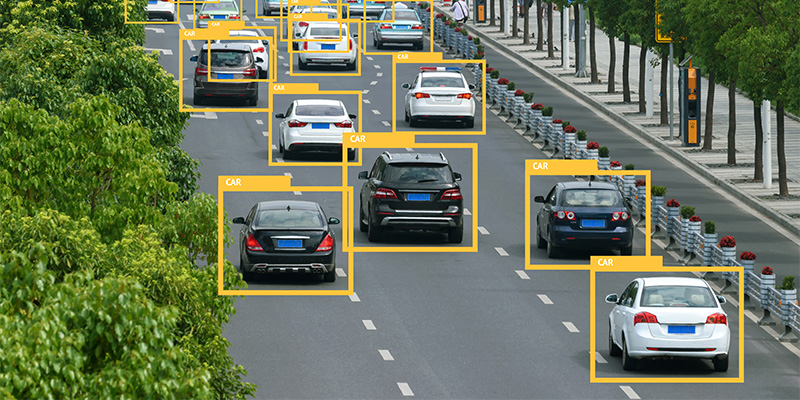
1. License Plate Recognition
License plate recognition (LPR) technology offers versatile solutions for managing vehicle traffic and parking across various environments, including parking garages, schools, municipalities, and retail store parking lots. This technology utilizes high-resolution cameras and sophisticated AI algorithms to detect, read, and record vehicle license plates. In parking garages, LPR enhances security and operational efficiency by automating access control, eliminating the need for manual ticketing systems and reducing congestion during peak hours. By instantly verifying whether a vehicle is authorized to enter, LPR systems streamline the entry and exit processes, facilitating a smoother flow of traffic.
In educational and government settings, LPR contributes to everyone’s safety by ensuring that only registered vehicles can enter the premises. This system can automatically alert security personnel if an unregistered or suspicious vehicle attempts to gain access, thereby bolstering the security protocols in place. Similarly, in retail environments, LPR can be used to manage parking lot security effectively, deterring theft and unauthorized access. Retail stores can also use this technology to offer premium parking services for frequent shoppers or to enforce parking rules efficiently, enhancing the customer experience while ensuring compliance with store policies. Across these scenarios, LPR not only reinforces security but also provides valuable data that can help manage parking resources more effectively.
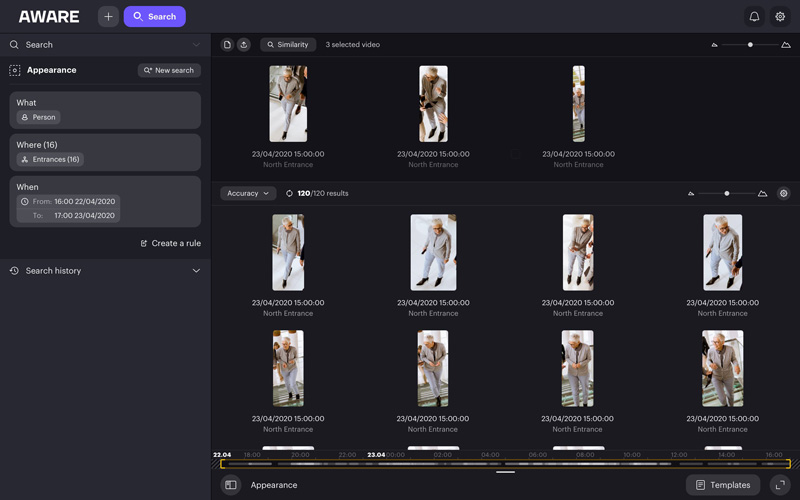
2. Appearance Search
With appearance search technology, operators are able to quickly locate a specific individual across a vast network of cameras, in real-time or recorded footage, by inputting physical descriptors such as clothing color, height, or other unique features. In settings where safety and quick response are crucial—such as airports, malls, or large public events—appearance search can swiftly pinpoint the location of a person of interest. For instance, in the scenario of a missing child in a busy shopping mall, security personnel can use appearance search to filter through hours of video footage in moments, focusing on individuals who match the child’s description, thereby speeding up the search process and increasing the chances of a safe recovery.
Appearance search extends beyond safety applications to enhance business operations and customer service. In large corporate or educational campuses, appearance search can help manage and locate personnel during emergencies, streamlining evacuation procedures and ensuring that all individuals are accounted for. This technology leverages deep learning algorithms that continuously improve in accuracy and speed with the ingestion of more data, showcasing a prime example of how AI-driven tools are reshaping the landscape of security and operational efficiency.
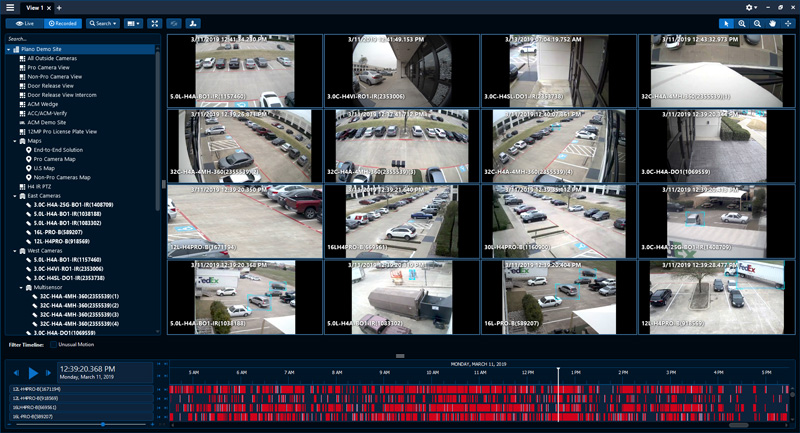
3. Object Detection
Object detection is a core capability within AI video analytics that involves identifying and categorizing various objects within video frames in real-time. This technology utilizes deep learning algorithms to recognize and differentiate between objects such as vehicles, people, animals, or any specific items that might be of interest within a surveillance environment. For instance, object detection can automatically alert security teams when unauthorized objects—or the absence of required ones—are detected in sensitive areas. This might include detecting an unattended bag in an airport or noticing the removal of expensive equipment from a restricted area. By providing real-time alerts, object detection enables immediate response to potential threats, enhancing security and situational awareness.
In the retail sector, object detection technology has transformative applications ranging from inventory management to enhancing customer experiences. Retailers can use object detection to monitor stock levels on shelves, automatically triggering alerts when replenishment is needed or identifying when items are placed in the wrong location to optimize inventory management and improve sales and customer satisfaction.
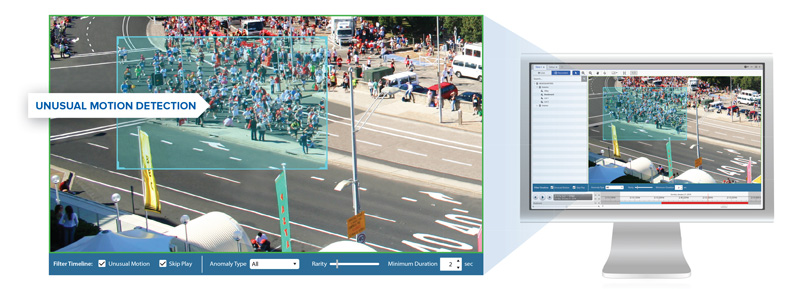
4. Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection in AI video analytics is crucial for identifying events or patterns that deviate from the norm within a video stream, offering a proactive approach to security and operational efficiency. This kind of analysis uses advanced algorithms to learn what normal activity looks like in a specific environment and can alert operators when anomalies occur. For example, anomaly detection can flag unusual activities such as someone entering a restricted area at an odd hour or a vehicle moving against the flow of traffic. These alerts allow security personnel to respond swiftly, potentially preventing incidents before they escalate. Anomaly detection can also highlight unexpected behaviors like prolonged loitering or unusual crowd formations, which might suggest potential theft or other disruptions.
Beyond security, anomaly detection has broader applications across various industries. In manufacturing, this technology is used to monitor equipment and processes for signs that deviate from standard operational parameters. Early detection of such anomalies can signify equipment malfunctions or process inefficiencies, allowing for prompt maintenance and reducing downtime, which in turn saves costs and maintains productivity levels.