How to Choose the Right Commercial Security Camera for Your Environment
With so many video surveillance camera models on the market, how do you know which is the most effective for your facility? In this comprehensive guide to commercial security cameras, we compare the features and use cases of the most common camera models.
Table of Contents:
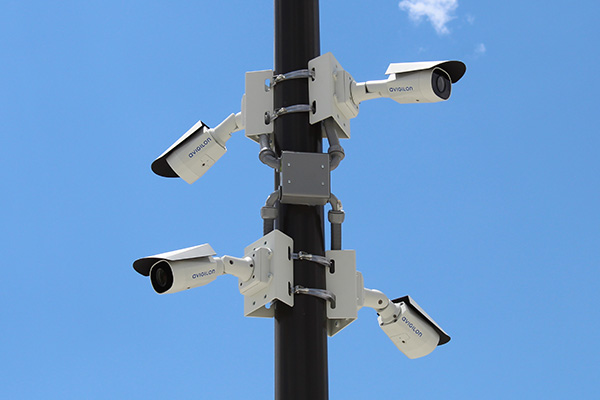

Bullet and Box Cameras
Bullet and box cameras are popular choices for surveillance due to their durability and versatility. These cameras are typically wired for power and data transmission, providing a reliable connection. They can be used both indoors and outdoors, making them suitable for various locations such as parking lots, entrances, and hallways. Bullet and box cameras are commonly used in K-12 schools to monitor common areas, higher education institutions for campus security, government facilities to safeguard entrances, enterprises to protect assets, and hospitals for parking lot surveillance.
Features
Design and Versatility: Bullet and box cameras typically have a cylindrical or rectangular shape, which makes them easily recognizable. They are designed to be mounted on walls, ceilings, or other surfaces and can be adjusted to capture specific areas or angles. The design of these cameras often allows for easy installation and positioning.
Weatherproof and Outdoor Use: Bullet and box cameras are commonly used for outdoor surveillance as they are designed to be weatherproof and withstand harsh environmental conditions. They are built with sturdy enclosures that protect the camera components from rain, dust, and extreme temperatures, making them suitable for monitoring exterior areas like parking lots, building perimeters, or construction sites.
Varifocal Lens: Many of these cameras come with a varifocal lens, allowing for adjustable focal length and zoom capabilities. This feature provides flexibility in adjusting the camera’s field of view and zooming in or out as needed, making them suitable for various surveillance scenarios.
Infrared (IR) Illumination: Most bullet/box cameras have built-in infrared LEDs, enabling them to capture clear video footage even in low-light or complete darkness. This night vision capability is crucial for round-the-clock surveillance in outdoor environments.
Long-Range Monitoring: Box and bullet cameras are often equipped with lenses that provide a long-range focal length. This allows them to capture detailed images and monitor objects or areas at a distance. They are commonly used in applications such as monitoring large parking lots, perimeters, or expansive outdoor areas.
Wide-Angle Coverage: While bullet/box cameras may not offer the same wide-angle coverage as dome cameras, they can still capture a broader field of view compared to some other camera types. This makes them suitable for monitoring long hallways, walkways, or corridors.
Integration with PTZ Cameras: In some cases, bullet and box cameras are used in conjunction with PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras. Bullet/box cameras can provide wide-area coverage, while PTZ cameras can be used for targeted monitoring or zooming in on specific areas of interest. This combination allows for comprehensive surveillance in large or complex environments.
When to Use Them
Perimeter Surveillance: Bullet/box cameras are commonly used for perimeter surveillance to monitor and secure the boundaries of a property or facility. They can be positioned along fences, walls, or building exteriors to detect and deter potential intruders.
Outdoor Monitoring: Bullet/box cameras are suitable for outdoor monitoring in various settings such as parking lots, construction sites, or public spaces. Their weatherproof design and infrared capabilities allow for reliable surveillance in challenging outdoor conditions.
Long-Distance Surveillance: Bullet/box cameras with long-range lenses are used for long-distance surveillance applications. They can monitor expansive outdoor areas, such as airports, seaports, or industrial sites, where long-distance monitoring is required.
Traffic Monitoring: Bullet/box cameras are deployed for traffic surveillance and monitoring on roads, highways, or intersections. They can capture clear video footage of vehicles, license plates, and traffic flow, assisting in traffic management and law enforcement.
Retail and Commercial Security: Bullet/box cameras are commonly used in retail stores, banks, offices, and commercial establishments. They can be positioned to monitor entrances, parking areas, cash registers, or high-value merchandise sections to deter theft and ensure security.
Critical Infrastructure Protection: Used to monitor critical infrastructure such as power plants, water treatment facilities, or telecommunications sites. They provide surveillance for essential equipment, entry points, or sensitive areas, helping to maintain security and prevent unauthorized access.
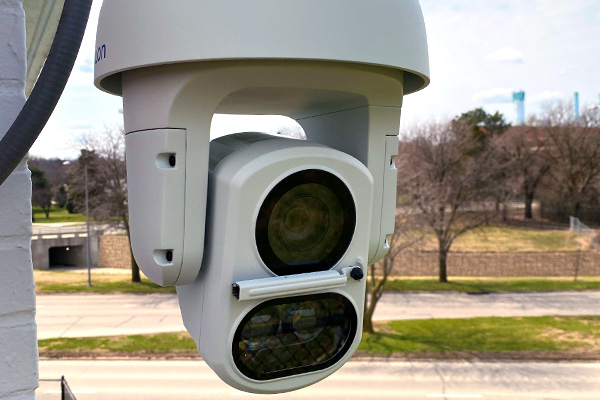

Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Cameras
Commercial pan-tilt-zoom security cameras (PTZ for short) offer excellent flexibility and coverage. As the name states, these cameras can be remotely controlled to pan, tilt, and zoom in on specific areas, providing a wide field of view. They are suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, making them ideal for monitoring large spaces, such as lecture halls, sports arenas, government buildings, enterprise campuses, and hospital corridors.
Features
360-Degree Coverage: PTZ cameras can rotate horizontally (pan), tilt vertically, and zoom in or out to provide comprehensive coverage and focus on specific areas or objects of interest. They can pan a full 360 degrees or even more, allowing them to monitor a wide area without blind spots. This feature is particularly useful for large open spaces, such as parking lots or courtyards.
Presets and Tours: PTZ security cameras often have the ability to set and recall preset positions. This means they can be programmed to automatically move and focus on specific areas or pre-defined points. Tours can also be set up, involving a sequence of pre-programmed movements to monitor different areas in a systematic manner.
Motion Tracking: Many PTZ security cameras include intelligent features such as motion tracking. When enabled, the camera can detect motion, track moving objects within its range, and keep them in the frame. This feature is useful for monitoring suspicious activities or following individuals as they move through an area.
Auto-Tracking: Some PTZ security cameras have advanced auto-tracking capabilities. They can automatically detect and track a moving object based on predefined criteria such as size, shape, or color. This feature is particularly valuable in situations where there is a need to monitor specific targets consistently, such as individuals in a restricted area.
High Zoom Capability: PTZ security cameras are equipped with motorized zoom lenses that allow for optical and digital zooming. This enables operators to focus on specific details or objects, even from a considerable distance. High zoom capability is particularly useful for capturing license plates, identifying individuals, or observing distant objects or areas.
Remote Control and Monitoring: PTZ security cameras can be controlled remotely using various methods such as a joystick, software interface, or mobile app. Operators can adjust the camera’s position, tilt, and zoom in real time, even from a different location. Remote monitoring capabilities enable security personnel to respond promptly to incidents or suspicious activities.
When to Use Them
Large Area Surveillance: PTZ cameras are ideal for monitoring large areas such as airports, industrial sites, or public spaces. Their ability to pan, tilt, and zoom allows operators to cover expansive areas effectively and focus on specific points of interest.
Perimeter Protection: PTZ cameras can be positioned at the perimeter of a facility to monitor and detect intrusions. They can scan the surroundings, track suspicious activities along the perimeter, and zoom in to gather detailed information when necessary.
Access Control Points: Commonly used at access control points such as gates, entrances, or checkpoints. They can provide clear identification of individuals, monitor access procedures, and record any suspicious behavior.
Event Monitoring: PTZ cameras are deployed in stadiums, concert venues, or large-scale events to ensure security and crowd management. Operators can monitor crowd movement, zoom in on specific incidents, and track potential security threats.
Alarm Response: PTZ cameras can be integrated with alarm systems. When an alarm is triggered, the camera can automatically move to a preset position or a specific area to capture relevant video footage, allowing security personnel to assess the situation quickly.
Critical Infrastructure Protection: PTZ cameras are used to secure critical infrastructure such as power plants, water treatment facilities or transportation hubs. Their versatility allows for effective monitoring of the infrastructure, identification of potential vulnerabilities, and response to security breaches.
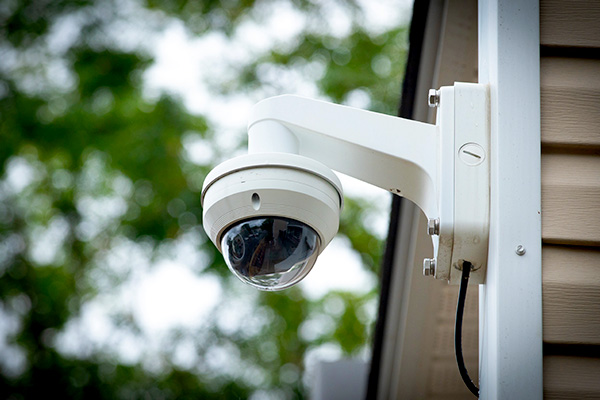

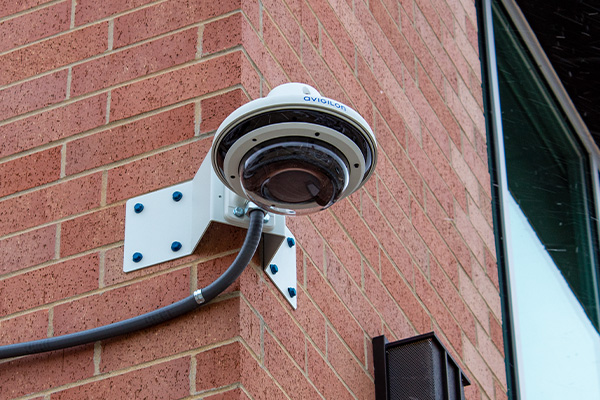
Dome Cameras
Dome cameras, as the name suggests, are designed in a dome-shaped housing, providing a discreet surveillance solution. These commercial security cameras can be mounted on ceilings or walls, offering a wide field of view and a deterrent effect on potential intruders. They are commonly used in educational institutions for classroom surveillance, government buildings for monitoring public areas, retail spaces, and hospitals for monitoring waiting rooms and entrances.
Features
Discreet and Vandal-Resistant: Dome cameras are designed to be inconspicuous and blend into the environment. The dome-shaped enclosure hides the direction of the camera, making it difficult for potential intruders or suspects to determine where the camera is pointing. This design helps to prevent tampering and vandalism, as the camera is often enclosed in a robust, impact-resistant casing.
Wide-Angle Coverage: Dome cameras typically offer a wide-angle lens that allows for a broad field of view. They can capture a larger area compared to some other camera types. This feature makes dome cameras suitable for monitoring open spaces, hallways, entrances, or areas where a broad view is required.
Indoor and Outdoor Use: Dome cameras are available in both indoor and outdoor variants. Outdoor dome cameras are designed to be weatherproof and can withstand harsh environmental conditions such as rain, dust, and extreme temperatures. They are often equipped with features like built-in heaters or fans to ensure proper operation in different weather conditions.
Infrared (IR) Illumination: Many dome cameras have built-in infrared LEDs that provide night vision capabilities. This allows the camera to capture clear video footage even in low-light or complete darkness. IR illumination is crucial for round-the-clock surveillance in outdoor areas or poorly lit environments.
Varifocal Lens: Dome cameras often feature a varifocal lens, which allows for adjustable focal length and zoom capabilities. This feature enables operators to adjust the camera’s field of view and zoom in or out as needed, providing flexibility in capturing specific details or monitoring different distances.
Pan and Tilt Adjustments: Some dome cameras offer limited pan and tilt adjustments within the enclosure. While not as versatile as PTZ cameras, these cameras can still provide some flexibility in adjusting the camera’s viewing angle without the need for physically repositioning the entire camera.
Easy Installation: Dome cameras are relatively easy to install and can be mounted on walls, ceilings, or even pendant mounts. The dome design also helps to conceal cables and wiring, providing a neater and more aesthetically pleasing installation.
When to Use Them
Indoor Surveillance: Dome cameras are commonly used for indoor surveillance in various settings such as offices, retail stores, banks, and educational institutions. Their discreet design allows for unobtrusive monitoring of sensitive areas without causing discomfort to employees, customers, or students.
Outdoor Surveillance: Suitable for outdoor surveillance in locations like parking lots, building exteriors, or public spaces. Their weather-resistant enclosures and vandal-resistant features make them reliable and durable for monitoring outdoor environments.
Traffic Monitoring: Can be used for traffic surveillance and monitoring, both in urban areas and on highways. They can capture video footage of intersections, roadways, or toll booths to monitor traffic flow, detect violations, and assist in traffic management.
Building Entrances and Lobbies: Dome cameras are commonly used at building entrances, lobbies, or access points to monitor and record people entering or exiting the premises. They can provide visual evidence of individuals, track visitor movements, and assist in access control procedures.

Panoramic and 360 Cameras
Panoramic, 360, and fisheye cameras are specialized devices that capture a 360-degree field of view, eliminating blind spots. These cameras are typically mounted on ceilings or mounted on walls and provide a comprehensive overview of the surroundings. They are commonly used in higher education institutions for monitoring large common areas, government facilities, warehouses, and hospital corridors.
Features
360-Degree Coverage: Panoramic cameras provide a complete view of the surroundings, capturing a full 360-degree or near-360-degree field of view. This eliminates blind spots and allows for comprehensive monitoring of large areas with a single camera.
Single Camera Solution: With a panoramic camera, a single camera can cover an area that might otherwise require multiple cameras. This reduces installation and maintenance costs, simplifies the wiring and infrastructure, and minimizes the number of devices to manage.
Distortion Correction: Panoramic cameras use advanced lens technology, such as fisheye lenses, to capture a wide field of view. These lenses introduce some distortion, but panoramic cameras often come with built-in software or hardware that corrects the distortion, resulting in a more accurate and usable video image.
Dewarping: Panoramic cameras typically provide dewarping capabilities. Dewarping is the process of correcting the captured fisheye image and converting it into different viewing modes, such as a single dewarped view, multiple dewarped views, or virtual PTZ views. This allows operators to view and navigate the captured video in a more intuitive and detailed manner.
Virtual PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom): Panoramic cameras offer virtual PTZ functionality, which allows users to digitally pan, tilt, and zoom within the captured wide-angle image. This enables operators to focus on specific areas of interest or zoom in on details, even after the video has been recorded.
Multiple Viewing Modes: Panoramic cameras provide various viewing modes to suit different surveillance needs. These modes may include a 360-degree overview, a split-screen view with multiple dewarped images, or a virtual PTZ view. Users can switch between these modes to optimize their monitoring and analysis.
Intelligent Video Analytics: Panoramic cameras often come with built-in intelligent video analytics capabilities. These analytics can detect and track moving objects, perform people counting, monitor crowd density, detect abandoned objects, and more thanks to their wide field of view.
When to Use Them
Large-Scale Monitoring: Panoramic cameras are well-suited for monitoring large areas such as airports, train stations, stadiums, or public squares. They can provide comprehensive coverage, reduce blind spots, and capture a wide range of activities within a single view.
Crowd Management: Panoramic cameras are used for crowd management and situational awareness in public spaces. They can monitor crowd density, detect overcrowding or bottleneck areas, and facilitate crowd flow management during events or in busy areas.
Perimeter Surveillance: Panoramic cameras are employed for perimeter surveillance, allowing operators to monitor the entire perimeter of a property or facility from a single camera. This is particularly useful for securing critical infrastructure, manufacturing sites, or high-security areas.
Retail Analytics: Panoramic cameras with intelligent video analytics can provide valuable insights for retail stores. They can analyze customer behavior, track foot traffic, monitor shopping patterns, and detect suspicious activities. These analytics help optimize store layout, improve customer service, and enhance security.
Wide-Angle Monitoring: Suitable for monitoring wide-angle views such as hallways, corridors, or open spaces. They can replace multiple traditional cameras and provide a more comprehensive view, reducing the overall camera count.
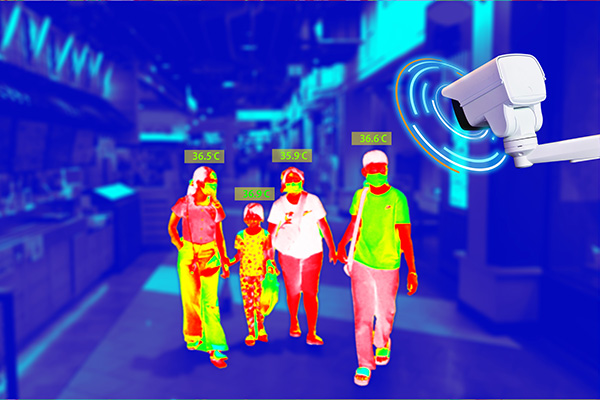

Thermal Cameras
A thermal camera, also known as a thermal imaging camera or infrared camera, utilizes heat-sensing technology to detect and visualize heat signatures. These cameras are excellent for detecting anomalies, even in complete darkness or challenging weather conditions. Thermal cameras are commonly used in institutions for perimeter security, identifying temperature variations in crowded areas, monitoring access points, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Features
Heat Detection: Thermal cameras detect and capture the thermal energy emitted by objects, allowing them to generate images based on temperature differences. This enables them to detect and visualize heat signatures, regardless of lighting conditions or obstructions like smoke, fog, or total darkness.
Night Vision: Thermal cameras provide excellent night vision capabilities since they rely on detecting heat rather than visible light. They can capture clear images even in complete darkness, making them ideal for 24/7 surveillance operations.
Wide Temperature Range: Thermal cameras can detect and measure a wide range of temperatures, typically from -20°C to several hundred degrees Celsius. This versatility makes them suitable for various applications, including fire detection, industrial monitoring, and perimeter security.
Unaffected by Lighting Conditions: Thermal cameras are not dependent on visible light, making them immune to lighting conditions such as bright sunlight, complete darkness, or glare. They can operate effectively in challenging lighting environments, ensuring continuous surveillance and reliable detection.
High Contrast Imaging: These cameras create images based on temperature differences, resulting in high contrast imaging. Objects with different temperatures are easily distinguishable, allowing operators to quickly identify potential threats or anomalies in the monitored area.
Motion Detection: Thermal cameras can detect motion based on changes in heat signatures. This feature is particularly useful for intrusion detection and perimeter security, as the cameras can generate alerts when a person or object enters a specific zone or crosses a virtual tripwire.
Analytics and Alarm Integration: Thermal cameras often come with built-in analytics software that can perform advanced functions such as object tracking, people counting, or temperature measurement. They can integrate with alarm systems to trigger alerts or actions based on specific events, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the security system.
When to Use Them
Perimeter Protection: Thermal cameras are widely used for perimeter protection in various applications, including critical infrastructure, industrial sites, or sensitive facilities. They can detect and alert operators to intrusions, trespassing, or unauthorized access, even in challenging lighting or weather conditions.
Border Surveillance: Thermal cameras play a vital role in border surveillance, helping to detect and monitor illegal crossings or smuggling activities. Their ability to detect human or animal heat signatures allows for efficient monitoring of vast border areas.
Fire Detection: Thermal cameras can be deployed for early fire detection in industrial settings, warehouses, or areas prone to wildfires. They can identify heat sources or temperature anomalies, enabling quick response and minimizing the risk of property damage or casualties.
Search and Rescue Operations: Thermal cameras are instrumental in search and rescue operations, especially in challenging environments or during night missions. They can help locate missing persons by detecting their heat signatures, aiding in swift and accurate rescue efforts.
Wildlife Monitoring: Thermal cameras are used for wildlife monitoring and conservation purposes. They can observe animal behavior, track animal movements, and detect the presence of endangered species in their natural habitats without disturbing them.
Energy Efficiency and HVAC Monitoring: Thermal cameras can assist in energy efficiency assessments and monitoring HVAC systems. They can identify areas of heat loss or excessive heat generation, allowing for targeted energy consumption and system maintenance improvements.
Choosing the Right Commercial Security Camera
When choosing the right security camera for your environment or facility, there are several questions you should consider. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a security camera that aligns with your unique requirements, ensuring optimal surveillance and protection for your environment or facility.
- Is indoor and/or outdoor monitoring required?
- What field of view is needed, and what level of detail is required?
- What are the lighting conditions like?
- What environmental factors need to be considered? (Consider weather resistance, temperature range, and the presence of dust or moisture.)
- Are additional features such as PTZ capabilities, analytics, or integration with other security systems necessary?
- What is your budget?
- What installation requirements are there?